 When installing two hard drives, it is necessary to check the jumper setting for the Master/Slave configuration. The jumper pins for Master/Slave can be found between the power connector and IDE ribbon cable connector. Every hard drive manufacturer has different pin configurations which is found on the information pasted in the hard drive itself
When installing two hard drives, it is necessary to check the jumper setting for the Master/Slave configuration. The jumper pins for Master/Slave can be found between the power connector and IDE ribbon cable connector. Every hard drive manufacturer has different pin configurations which is found on the information pasted in the hard drive itself
- Slave is for the second hard drive.

The platters are often made of an aluminum alloy and have a thin magnetic- media coating on both sides. After coating, the platters are polished and given another thin coating of graphite for protection against mechanical damage caused by physical contact between the data heads and the platter surface. The R/W heads "float on a cushion of air" above the platters, which spin at 3500 to 12,000 revolutions per minute (rpm). The distance (flying height) between the heads and the disk surface is less than the thickness of a fingerprint.
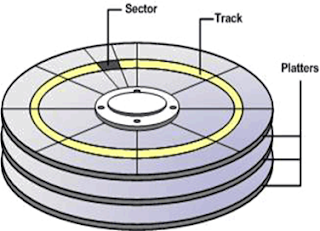
Hard disks are organized as a concentric stack of platters. The data is stored on concentric circles on the surfaces known as tracks. Sections within each track are called sectors. A sector is the smallest physical storage unit on a disk and typically it will hold 512 bytes of data. The disk itself can't handle smaller amounts of data than one sector. As the platters spin, the drive heads move in toward the center surface and out toward the edge. In this way, the drive heads can reach the entire surface of each platter. Reading from 2 tracks implies a realignment of the reading heads, thus it takes longer than reading a single track.
Hard Disk Basics
-The first IBM hard disk drives came out in the late 1970s and early 1980s and were code-named "Winchester." The original design concept included two 30-MB units in one enclosure: 30-30 (hence Winchester, after the well-known rifle cartridge popular in western movies). The PC-XT was the first personal computer to include a hard disk. They were called fixed disks because they were not removable by the end user, like a floppy. (Old mainframe computers had hard platters that were removable by a trained technician.) The Winchester technology is the forerunner of all PC fixed disks. - hard disks use a technology called magnetic recording scheme in writing a data, same is true with cassette tapes. In a hard disk, the read/write head "flies" over the disk, never actually touching it.

NOTE: For more information and clarification with regard on this topics, feel free to read “A+ Certification Training Kit / Microsoft Corporation.--3rd Ed.” PUBLISHED BYMicrosoft PressA Division of Microsoft CorporationOne Microsoft WayRedmond, Washington 98052-6399 Copyright © 2001 by Microsoft Corporation








No comments:
Post a Comment